The Linux command is a utility of the Linux operating system. All basic and advanced tasks can be done by executing commands. The commands are executed on the Linux terminal. The terminal is a command-line interface to interact with the system, which is similar to the command prompt in the Windows OS. Commands in Linux are case-sensitive.
Linux Directory Commands
1. pwd Command
The pwd command is used to display the location of the current working directory.
Syntax:
pwd
Output:

2. mkdir Command
The mkdir command is used to create a new directory under any directory.
Syntax:
mkdir <directory name>
Output:

3. rmdir Command
The rmdir command is used to delete a directory.
Syntax:
rmdir <directory name>
Output:

4. ls Command
The ls command is used to display a list of content of a directory.
Syntax:
ls
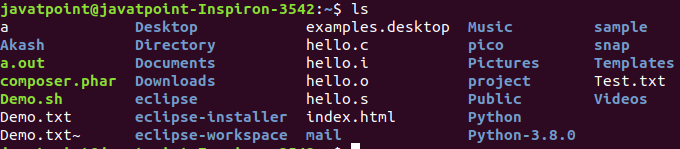
Output:
5. cd Command
The cd command is used to change the current directory.
Syntax:
cd
Output:

Linux File commands
6. touch Command
The touch command is used to create empty files. We can create multiple empty files by executing it once.
Syntax:
touch <file name>
touch <file1> <file2> ....
Output:
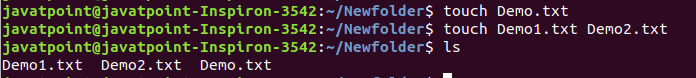
7. cat Command
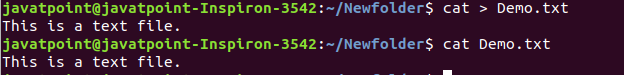
The cat command is a multi-purpose utility in the Linux system. It can be used to create a file, display content of the file, copy the content of one file to another file, and more.
Syntax:
cat [OPTION]... [FILE]..
To create a file, execute it as follows:
- cat > <file name>
- // Enter file content
Press “CTRL+ D” keys to save the file. To display the content of the file, execute it as follows:
Output:
cat <file name>
8. rm Command
The rm command is used to remove a file.
Syntax:
rm <file name>
Output:

9. cp Command
he cp command is used to copy a file or directory.
Syntax:
To copy in the same directory:
cp <existing file name> <new file name>
To copy in a different directory:
Output:

10. mv Command
The mv command is used to move a file or a directory form one location to another location.
Syntax:
mv <file name> <directory path>
Output:

11. rename Command
The rename command is used to rename files. It is useful for renaming a large group of files.
Syntax:
rename 's/old-name/new-name/' files
For example, to convert all the text files into pdf files, execute the below command:
- rename ‘s/\.txt$/\.pdf/’ *.txt
Output:
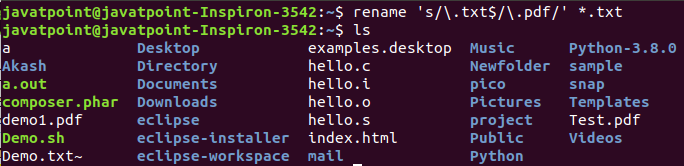
Linux File Content Commands
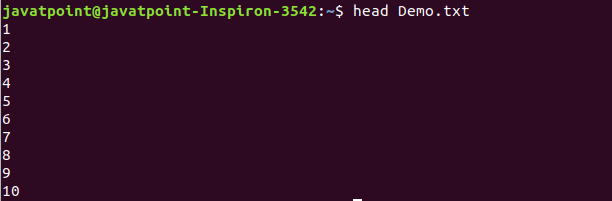
12. head Command
The head command is used to display the content of a file. It displays the first 10 lines of a file.
Syntax:
head <file name>
Output:
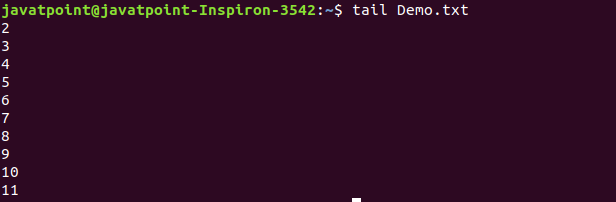
13. tail Command
The tail command is similar to the head command. The difference between both commands is that it displays the last ten lines of the file content. It is useful for reading the error message.
Syntax:
tail <file name>
Output:
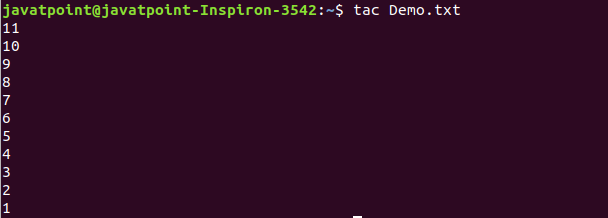
14. tac Command
The tac command is the reverse of cat command, as its name specified. It displays the file content in reverse order (from the last line).
Syntax:
tac <file name>
Output:
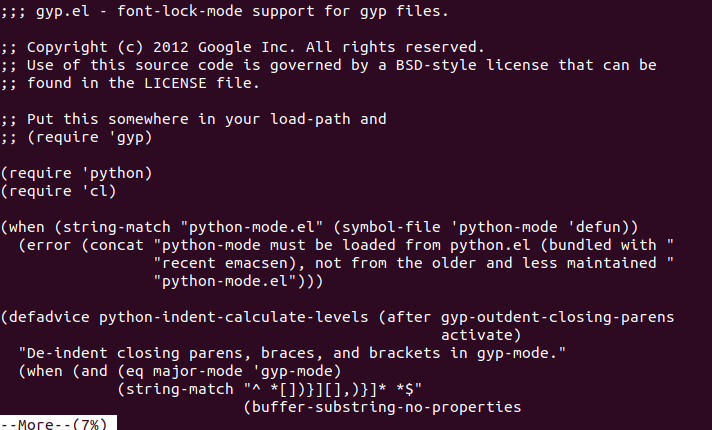
15. more command
The more command is quite similar to the cat command, as it is used to display the file content in the same way that the cat command does. The only difference between both commands is that, in case of larger files, the more command displays screenful output at a time.
In more command, the following keys are used to scroll the page:
ENTER key: To scroll down page by line.
Space bar: To move to the next page.
b key: To move to the previous page.
/ key: To search the string.
Syntax:
more <file name>
Output
Leave a comment